Why do we remove hair?
In today’s fast-paced modern world, people from all walks of life, including professionals, want to put their best foot forward and aspire to look beautiful. Most notably, for actors, dancers, musicians, stage performers, and all those who are in the show business or limelight, it is not enough to look presentable, the key to their success is linked to how attractive and trendy they look. Hair removal is one of the most common cosmetic trends today.
Over 50 years ago, Rox Anderson and John Parrish were the first two Harvard dermatologists who proposed the theory of selective photothermolysis. It highlighted the concept of targeting a particular chromophore based on its absorption spectra and size. The first successful use of a normal-mode ruby laser for long-term and permanent hair removal was done in 1996.
Techniques of hair removal
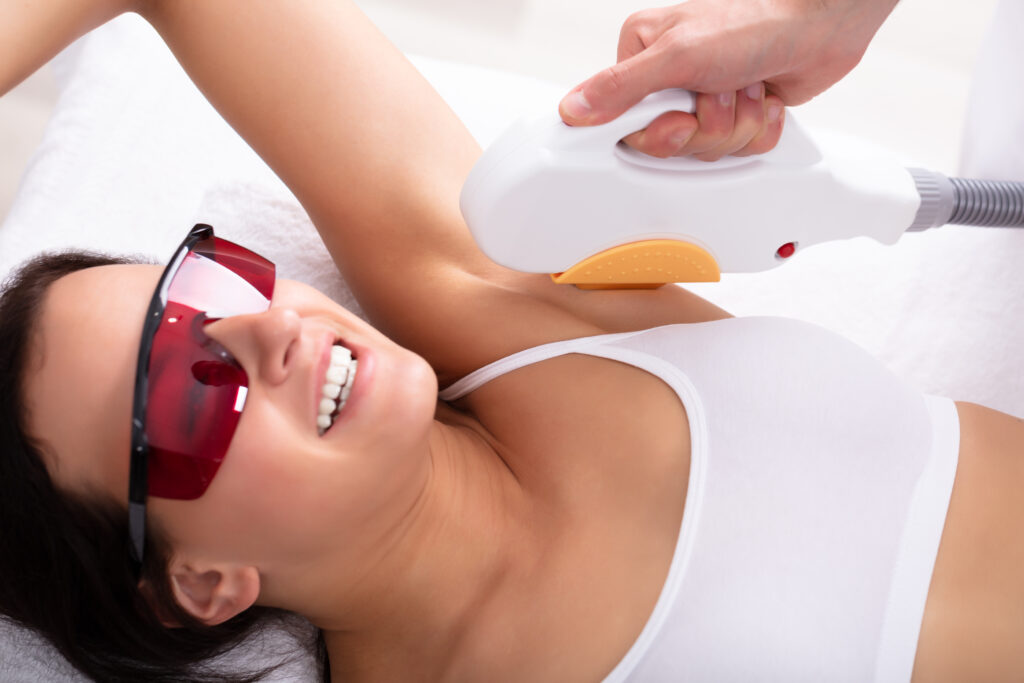

Today removing unwanted body hair has become a worldwide phenomenon. Before the introduction of the laser hair removal (LHR) technique, several other procedures such as plucking, shaving, waxing or bleaching, were in vogue. However, today LHR has become one of the most sought after cosmetic procedures. In fact, using laser or other light-based technology for removing unwanted hair, is one of the most common cosmetic procedures and it is in high demand.
Threading
In few cultures, cotton thread is used to remove hair and is more popularly known as threading. However, these methods of removing hair are neither permanent nor convenient.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis is another technique that uses a fine needle and electrical current to destroy the hair follicle and remove hair permanently. This approach can remove all types of hair. However, since approach is tedious and depends on the operator, it is not useful in treating large areas.
FDA has currently cleared eflornithine or DFMO (a-difluoromethylornithine), which is a topical inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase that slows down the rate of hair growth. It is used for the removal of unwanted facial hair. Let us examine in detail the process of LHR, the hair follicle, and the factors involved in its treatment.
What is hair growth?
We present below an overview of the fundamentals of hair follicle anatomy and physiology, the procedure for selection of patients, preoperative preparation, laser safety and the impact of laser devices and post-operative care.
The anatomy of a hair follicle typically consists of an infundibulum, isthmus, and inferior segments. An infundibulum is the hair follicle orifice to the insertion of the sebaceous gland. The isthmus is the insertion of the sebaceous gland to the insertion of the arrector pili muscle, while the inferior is the insertion of the arrector pili to the base of the hair follicle.
A programmed cycle that depends on the anatomical location controls the hair follicle. The derma papilla helps form the hair shaft and provides neurovascular support to the base of the follicle.
The hair cycle has three phases, known as anagen, catagen and telogen. The first phase, or anagen, is a period of active growth in which the hair shaft lengthens. The second phase, or the catagen is when the lower part of the hair follicle goes through apoptosis. The third phase or the telogen, is the resting period, followed by anagen and regrowth. Regrowth of hair depends on the stem cells inside or near the hair bulb matrix.
Lanugo, vellus and terminal hairs are the three main types of hair. Lanugo is the hair that is found on a fetus and shed during the neonatal phase, while vellus is usually non-pigmented and has a diameter of 30 to 50 μm, while terminal hair shafts are between 150 to 300 μm in diameter.
The type of hair is capable of change, for example, from vellus to terminal hair at puberty or terminal to vellus hair in androgenic alopecia. Hair color is dependent on the amount and type of pigment in the hair shaft. Melanocytes located in the upper part of the hair bulb and outer root sheath of the infundibulum produce two kinds of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumalinin is brown-black pigment and pheomelanin is red pigment.
What is unwanted body hair?
What is referred to as excessive or unwanted body hair actually depends on cultural aspects. However, there are two basic types: hirsutism and hypertrichosis. Hirsuitism is the abnormal growth of terminal hair among women and is androgen dependent. It is in male pattern and occurs on the face and chest. Hypertrichosis refers to excess hair growth in any part of the body that is not androgen-dependent. Besides, the above, grafts and flaps that are used during skin surgery, can result in hair in an area that can cause functional impairment and a displeasing appearance.
Are you a performance artist or athlete suffering from excessive or unwanted hair?
Are you tired of tweezing, waxing, and shaving ingrown hair again and again?
Are you looking for a solution to remove unwanted and excessive hair permanently?
Read on. Laser hair removal is one of the most popular ways to remove excess hair. We all know how irritating and unpleasant it is to have unwanted hair on the face and body. Plucking, tweezing, waxing, and shaving are temporary. Even electrolysis can be painful and time-consuming. Laser hair removal, however, is permanent and suitable for all skin types and tones.
The Mechanics of Laser Hair Removal
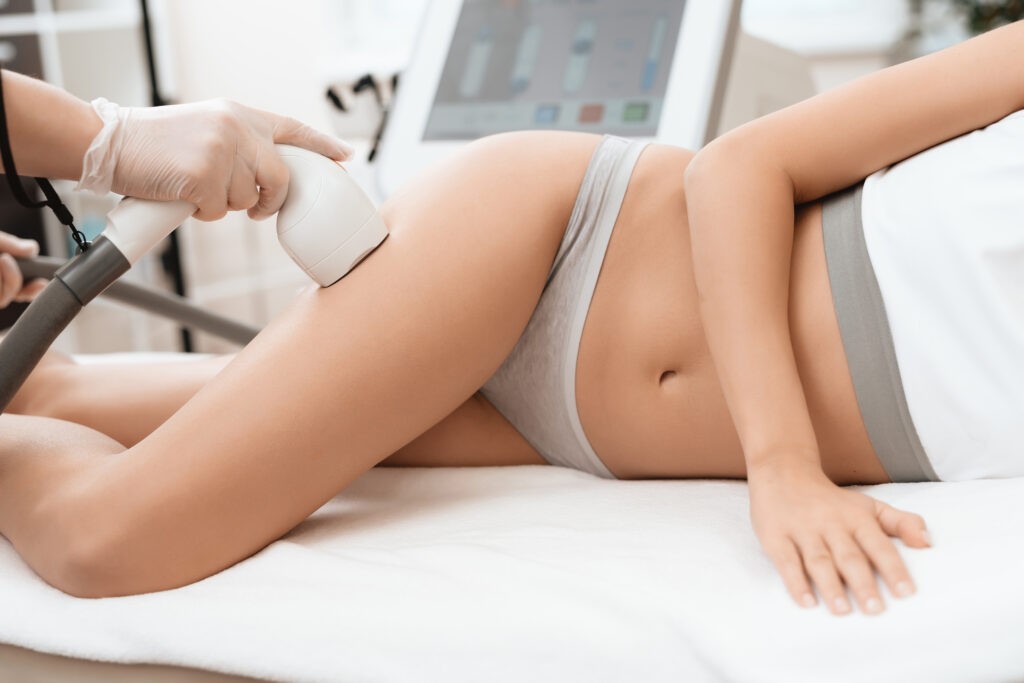

Precise targeting of pigmented hair follicles is possible through selective photothermolysis and by using the melanin of the hair shaft as a chromophore. The absorbance spectrum of melanin matches wavelengths in the red and near-infrared (IR) portions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
In order to attain permanent hair removal, the biological target is the follicular stem cells located in the bulge area or the dermal papilla. Due to the slight separation of the chromophore and desired target, it requires the diffusion of heat from the chromophore to the desired target for destruction. This requires a longer laser pulse duration than if the actual chromophore and desired target are identical.
It is much easier to achieve temporary LHR using lower fluences. When the follicular stem cells are not completely destroyed, temporary LHR can take place through induction of a catagen-like state in pigmented hair follicles. Long-term hair removal depends on the color of hair, skin, and tolerated fluence. When optimal treatment parameters are used, approximately 15-30% long-term hair loss may be observed with each treatment.
Are you considering Laser Hair Removal?
Our team of experts has the requisite qualifications and experience to guide you in this regard. We offer you a painless Laser Hair Removal session with ALMA SHR. You will also find that Laser Hair Removal in Scarborough is more affordable than in GTA. Find out more and book your consultation at 647-660-0860 or email us at Getbeautifulclinic@gmail.com.
